"Nothing to see here, folks
This long weekend was literal hell for millions in the American West. California, Nevada, Arizona, Oregon, and Washington are suffering from dangerous heat, wildfire and smoke unlike anything they’ve ever seen. |
| Californian Wildfires, 2019 |
Scientists attribute the unprecedented intensity of these events to human-caused climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions have made the atmosphere in these areas much hotter and drier than it used to be. “We’re living in a fundamentally climate-altered world,” MIT Technology Review noted last month, citing a multitude of peer-reviewed research about how climate change exacerbates extreme heat and wildfire. These so-called “compound climate events” are only predicted to get worse if greenhouse gas emissions continue unabated.
Every American should be aware of these basic scientific facts when reading about the devastation of this weekend’s record-breaking extreme weather. But most of the major newspaper stories about the Labor Day Weekend from Hell don’t contain any climate-related information. Why?
 |
| Melting Siberian permafrost |
Three major newspaper stories. Zero climate mentions.
Section A, page 12 of today’s New York Times contains a big story about the unprecedented weather pummeling California. Titled “Extreme Heat Turns State Into a Furnace,” the piece contains more than 1,700 words of devastating detail about how heat, fire, and toxic air are affecting people in the state. But none of those details were about why things are getting so bad. None of those words were “climate change.”
The Associated Press’s article today is similar. Titled “Scorched earth: Record 2 million acres burned in California,” it contains 1,100 words about the weather’s unprecedented nature. It lists several different record-breaking data points, and quotes state officials saying how “unnerving” it is to have broken these records so early in the wildfire season. And yet this article—which will be re-published this morning in newspapers across the country—also does not mention the reason why these records might be happening.
The Washington Post also has an article about unprecedented
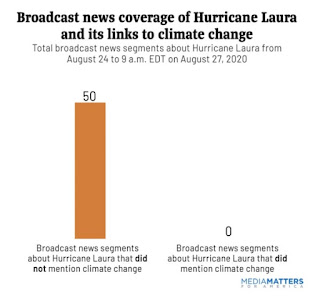 |
| News coverage of Hurricane Laura analysed |
“This is one of the largest and most dangerous fires in the history of Fresno County,” the local fire chief said. “I don’t think everyone understands that.”
Newspapers often ignore basic climate science in extreme weather stories
News outlets like the Times, the Post, and the AP have climate reporting teams. These teams all publish important stories about how the climate crisis fuels extreme weather across the country. The Times in particular has increased its climate coverage substantially in the last few years, according to data from the University of Colorado Boulder."
Related: Trump and Biden: Little room for climate change in US election (excerpt): DW
role of media, journalists, #California, #wildfire, #bushfires, permafrost, hurricanes, cyclones, #jailclimatecriminals,







